Radon Testing

What is Radon Gas?
Radon gas exposure occurs within residences, schools, and various structures. The gas enters indoors through foundation cracks and holes, becoming trapped. When radon is detected indoors, it can be controlled using proven and safe methods.
Indoor radon exposure is a significant concern as prolonged inhalation of radon gas has been linked to lung cancer. To address this risk, it is crucial to employ effective mitigation techniques. Certified professionals can implement ventilation systems and other proven methods to regulate and reduce radon levels, ensuring a safer indoor environment.
Awareness of radon gas and its potential health implications is essential for homeowners and building occupants. Regular radon testing is recommended to monitor indoor air quality, and if elevated levels are detected, prompt action is necessary to implement mitigation measures. By adopting verified and safe techniques, the threat of radon exposure can be minimized, contributing to healthier living and working environments.
How to lower the Radon level in your home
Since there is no known safe level of radon, there can always be some risk. But the risk can be reduced by lowering the radon level in your home.
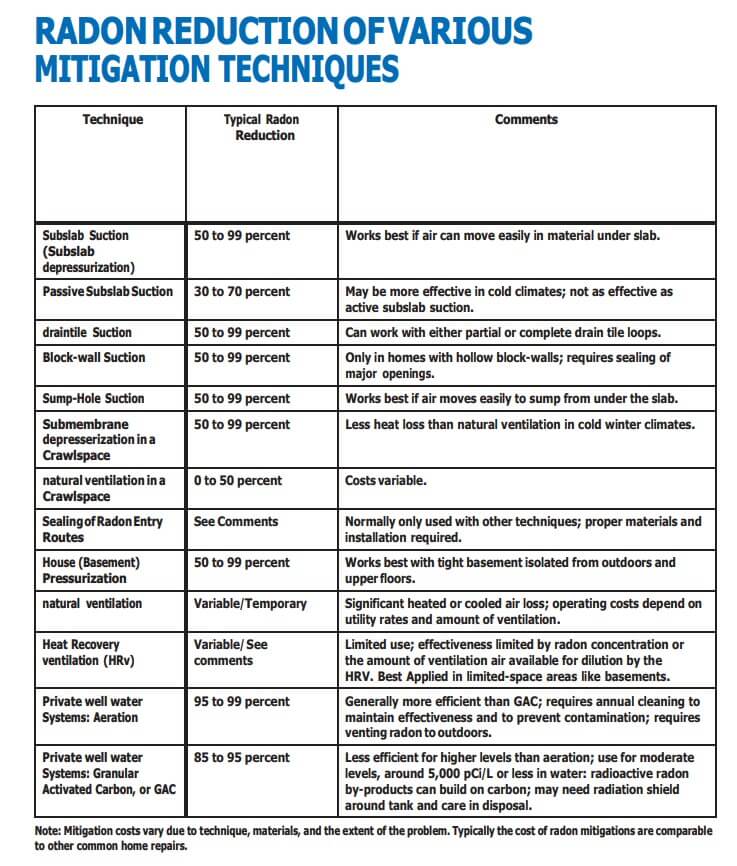
There are several proven methods to reduce radon in your home, but the one primarily used is a vent pipe system and fan, which pulls radon from beneath the house and vents it to the outside. This system, known as a soil suction radon reduction system, does not require major changes to your home. Sealing foundation cracks and other openings makes this kind of system more effective and cost-efficient. Similar systems can also be installed in houses with crawl spaces. Radon contractors can use other methods that may also work in your home. The right system depends on the design of your home and other factors.
Ways to reduce radon in your home are discussed in EPA’s Consumer’s Guide to Radon Reduction. You can get a copy at -about-radon https://www.epa.gov/radon/publications-about-radon.
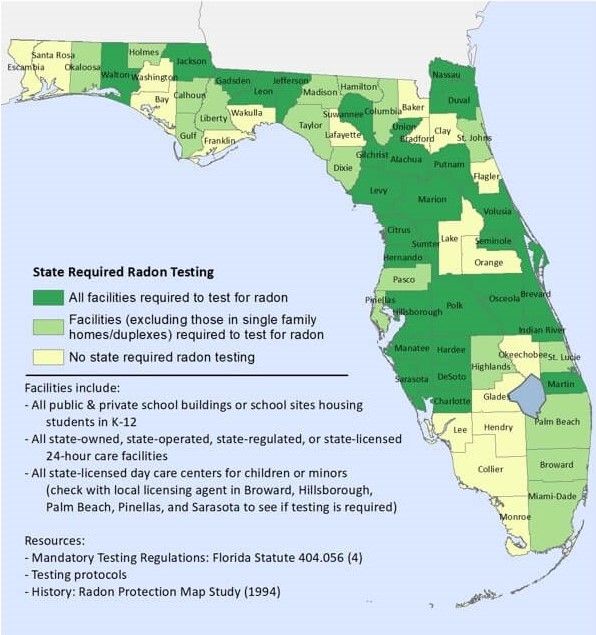
Florida Radon Testing Requirements
U.S. SURGEON GENERAL HEALTH ADVISORY
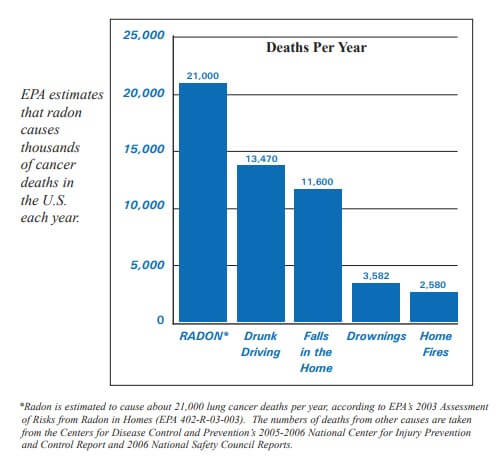
Indoor radon is the second-leading cause of lung cancer in the United States and breathing it over prolonged periods can present a significant health risk to families all over the country. It’s important to know that this threat is completely preventable. Radon can be detected with a simple test and fixed through well-established venting techniques.
Radon and home renovations
If you are planning any major structural renovation, such as converting an unfinished basement area into living space, it is especially important to test the area for radon before you begin the renovation. If your test results indicate a radon problem, radon- resistant techniques can be inexpensively included as part of the renovation. Because major renovations can change the level of radon in any home, always test again after work is completed.
There Are Two General Ways to Test Your Home for Radon
Short-Term Testing
The quickest way to test is with short-term tests. Short-term tests remain in your home from two to 90 days, depending on the device. There are two groups of devices which are more commonly used for short-term testing. The passive device group includes alpha track detectors, charcoal canisters, charcoal liquid scintillation detectors, and electret ion chambers. The active device group consists of different types of continuous monitors.
Long-Term Testing
Long-term tests remain in your home for more than 90 days. Alpha track and electret ion chamber detectors are commonly used for this type of testing. A long-term test result is more likely to tell you your home's year-round average radon level than a short-term test. If time permits (more than 90 days), long-term tests can be used to confirm initial short-term results. When long-term test results are 4 pCi/L or higher, EPA recommends fixing the home.
What Radon Test Results Mean
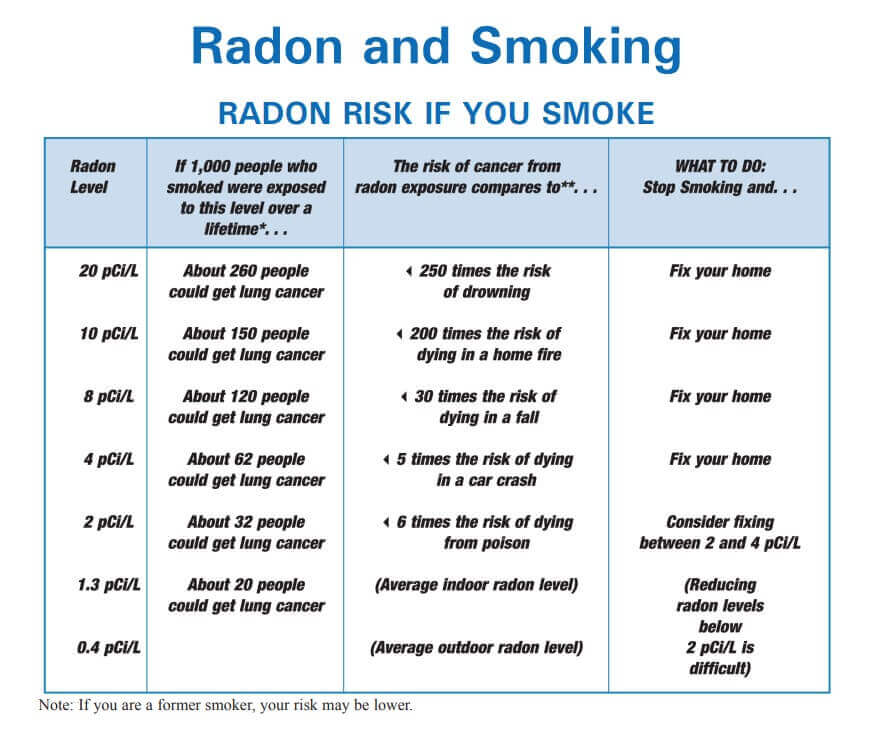
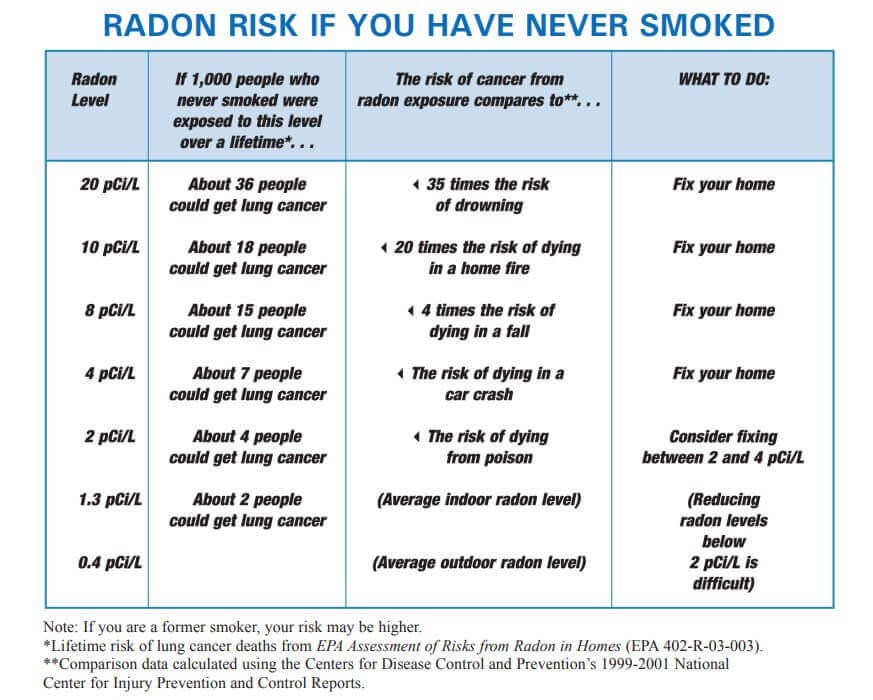
The average indoor radon level is estimated to be about 1.3 pCi/L, and about 0.4 pCi/L of radon is normally found in the outside air. The U.S. Congress has set a long-term goal that indoor radon levels be no more than outdoor levels. While this goal is not yet technologically achievable in all cases, most homes today can be reduced to 2 pCi/L or below.
Sometimes short-term tests are less definitive about whether or not your home is above 4 pCi/L. This can happen when your results are close to 4 pCi/L. For example, if the average of your two short-term test results is 4.1 pCi/L, there is about a 50% chance that your year-round average is somewhat below 4 pCi/L. However, EPA believes that any radon exposure carries some risk—no level of radon is safe. Even radon levels below 4 pCi/L pose some risk, and you can reduce your risk of lung cancer by lowering your radon level.
If your living patterns change and you begin occupying a lower level of your home (such as a basement) you should retest your home on that level. Even if your test result is below 4 pCi/L, you may want to test again sometime in the future.

Take control of your indoor air quality today!
Schedule a comprehensive radon test to safeguard your home and your loved ones. Our certified experts are ready to provide you with accurate results and guide you through any necessary mitigation measures. Don't compromise on the air you breathe – act now for a healthier and safer living environment. Contact us to schedule your radon test and make informed decisions about your home's well-being. Your peace of mind is just a click away!
Call Now!Request Inspection